What is Supply Chain Management: A Practical Guide

Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the art and science of getting a product from its very first spark of an idea all the way into a customer's hands. It’s the entire journey—from sourcing raw materials and building the product to managing inventory and making sure it gets delivered on time.
Think of it as the master plan, the connective tissue linking suppliers, manufacturers, warehouses, and retailers into one cohesive, flowing system.
Jump To Section

Earn As You Learn
Earn 25% commission when your network purchase Uplyrn courses or subscribe to our annual membership. It’s the best thing ever. Next to learning,
of course.
Decoding The Supply Chain Journey
So, what really is supply chain management?
Imagine you order a new pair of sneakers online. SCM is the invisible, globe-spanning network that took cotton, rubber, and dye and turned them into the shoes on your feet. It's the meticulous planning that ensured the materials were sourced ethically, the components were manufactured to spec, the shoes were assembled correctly, and they were shipped across the world to land on your doorstep.
This process is so much more than just trucks and warehouses; it’s a complex dance of planning, execution, and constant tweaking. The ultimate goal is simple: deliver the right product to the right place at the right time—all at the right cost.
When done well, SCM becomes a company's secret weapon. It slashes waste, drives down costs, and keeps customers happy. The industry's massive scale reflects its importance; the global supply chain management market was valued at an eye-watering $28.98 billion in 2022, with projections hitting nearly $62 billion by 2030.
The Five Core Pillars of Supply Chain Management
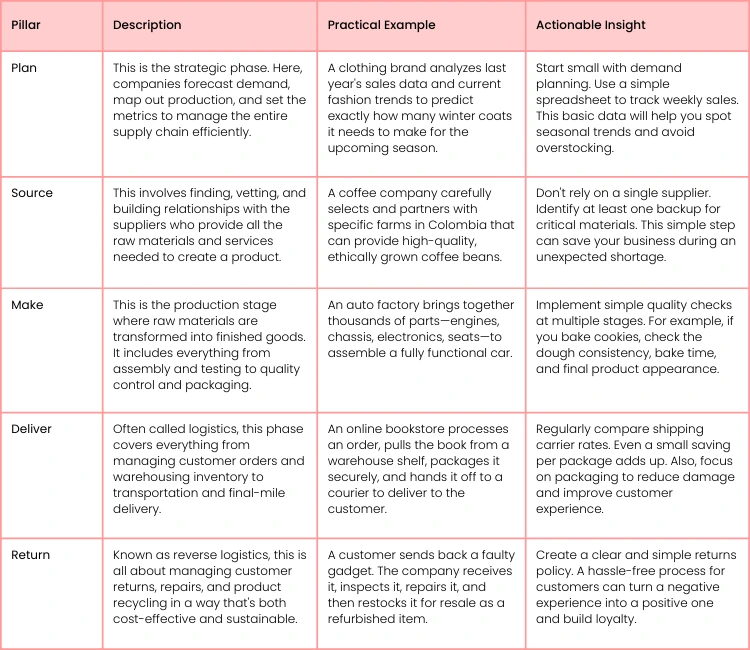
To really get a handle on SCM, it helps to break it down into five core stages. Each pillar is a critical phase in a product's life, and they all need to work in perfect harmony for the whole system to run smoothly. For anyone looking to get deeper into the mechanics, understanding these core operations management principles is the perfect place to start.
A well-managed supply chain doesn’t just move products; it moves information and value. Visibility and communication between these five pillars are what separate a good supply chain from a great one.
Getting a firm grasp on these concepts is essential for anyone in business. For those looking for practical insights, especially in the digital space, this guide to mastering supply chain management in e-commerce is a fantastic resource.
Here's a quick look at the five pillars that form the foundation of any supply chain.
Understanding Core SCM Components and Processes
Now that we've got the five pillars of supply chain management down, let's pop the hood and look at the engine that makes everything run. A successful supply chain isn't just a list of steps; it’s a living, breathing network where different parts and processes work together seamlessly. Each piece has a job, from sourcing raw materials to guessing what customers will want to buy next month.
Think about a car manufacturer for a second. Its supply chain is a sprawling global beast. To build just one car, they need to pull in thousands of individual parts—steel from one country, microchips from another, and leather from a third. Getting that right means mastering a few key processes.
Procurement: Sourcing the Building Blocks
Procurement is the art and science of getting all the goods, services, and work a company needs to function. It’s way more than just "buying stuff". It's about finding the right suppliers, negotiating smart deals, and making sure you have a steady stream of quality materials. A sloppy procurement process can bring the entire production line to a screeching halt.
- Practical Example: A local bakery needs high-quality flour. Instead of just buying the cheapest option, their procurement process involves testing samples from three different mills, negotiating a bulk discount for a six-month supply, and setting up a reliable weekly delivery schedule.
- Actionable Insight: Create a simple supplier scorecard. Rate your suppliers on key factors like on-time delivery, quality, and communication. Review it quarterly to ensure you're working with the best partners.
Logistics: The Physical Journey of Goods
Once you've bought all your materials, they need to get from point A to point B. That's where logistics comes in. This is the part of the supply chain that handles the physical movement of goods, from their starting point all the way to the final customer. It covers everything from transportation and warehousing to managing the fleet of trucks. It’s the hands-on, on-the-ground action most people picture when they hear "supply chain".
- Practical Example: A furniture company must ship a sofa from its factory in North Carolina to a customer in California. Their logistics team decides the most cost-effective method is via freight train to a regional hub and then a local delivery truck for the final mile, all while providing the customer with a tracking number to follow the journey.
- Actionable Insight: Optimize your packaging. Use the smallest, lightest box possible that still protects your product. This can significantly cut shipping costs charged by carriers who factor in dimensional weight.
Inventory and Demand Planning
Okay, so you have the materials and a way to move them. But do you have the right amount? Inventory management is the delicate balancing act between the cost of holding onto stock and the risk of running out. If you have too much inventory, you're tying up cash and paying for storage. Too little, and you're looking at lost sales and frustrated customers.
This ties directly into demand planning, which is all about predicting what your customers will want in the future. By looking at past sales data, market trends, and even seasonal changes, companies can make educated guesses about how much of a product they need to make.
- Practical Example: A toy company uses demand planning to ramp up production of its most popular action figure starting in August, anticipating the holiday shopping rush from October to December. They analyze sales data from previous years to forecast exactly how many units they'll need.
- Actionable Insight: Implement the "ABC" inventory method. Categorize your products: 'A' for high-value, low-quantity items; 'B' for moderate; and 'C' for low-value, high-quantity. Focus your management efforts on the 'A' items, as they have the biggest financial impact. Different approaches like OEM and ODM manufacturing strategies also play a huge role in aligning production with these forecasts.
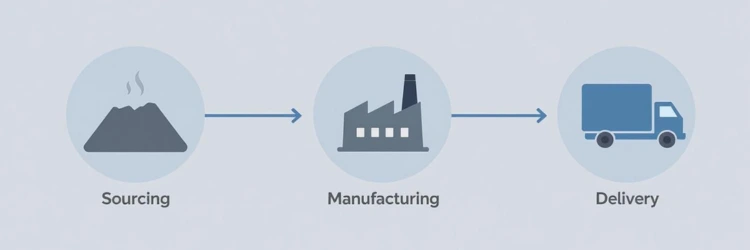
To really see how these stages connect, just follow the journey of a smartphone from a pile of raw materials to the palm of your hand.
This simple diagram shows the basic path a product takes, but it also highlights how sourcing, manufacturing, and delivery are separate steps that are completely dependent on each other.
The Technology and KPIs Driving Modern Supply Chains
Long gone are the days of clipboards and spreadsheets. Today’s supply chains are powered by some seriously smart technology that gives companies a bird's-eye view of their entire network. This digital shift means businesses can finally get ahead of problems instead of just reacting to them.
It all comes down to data. Every time a package is scanned, a truck’s location is updated, or an order is placed, it creates a digital footprint. The right tech scoops up this ocean of information, makes sense of it, and helps people make smarter, faster decisions.
Core Technologies That Power SCM
While there's a whole universe of software out there, a few key systems form the backbone of nearly every modern supply chain. They all work together to give everyone—from the factory floor to the C-suite—a single source of truth.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: Think of an ERP as the central nervous system of a business. It connects all the vital organs—finance, HR, manufacturing, and supply chain—into one unified system. This breaks down departmental silos and makes sure everyone is working from the same real-time information.
- Practical Example: When a sales rep enters a new order into the ERP, it automatically alerts the warehouse to prepare the shipment, notifies the factory to produce more if stock is low, and informs the finance team to send an invoice.
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): A WMS is the brain of the warehouse. This specialized software tells staff the most efficient routes for picking items, figures out the best way to stack pallets to save space, and automates everything from receiving new inventory to shipping out orders.
- Practical Example: Amazon's WMS directs warehouse workers on the optimal path to pick items for multiple orders at once, drastically reducing walking time and speeding up fulfillment.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning have also moved from "nice-to-have" to "can't-live-without". For example, major retailers now use AI to predict demand for winter coats by analyzing weather forecasts, social media chatter, and past sales data with incredible accuracy. That kind of foresight is a massive competitive advantage.
Measuring What Matters: Key Performance Indicators
Technology gives you the data, but Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) tell you if you're actually winning. KPIs are the specific metrics you track to gauge the health and efficiency of your supply chain. When you focus on the right ones, you can turn a mountain of operational data into a simple, clear scorecard.
KPIs are more than just numbers on a dashboard. They're the signposts that tell you where your supply chain is excelling and where it needs a tune-up, turning raw data into real-world action.
Here are a few of the most critical KPIs in supply chain management:
- Order Fulfillment Rate: This is the percentage of orders you ship completely and on time. A high number here means you’re running a tight ship and keeping customers happy. If it’s low, you can dig into why—is it an inventory issue? A supplier delay?
- Actionable Insight: Start by tracking your on-time shipment percentage. If an order is late, make a note of the reason. After a month, you'll see a pattern (e.g., "Supplier X is always late") that you can act on.
- Inventory Turnover: This metric tells you how many times you sell through your entire stock in a given period. A higher number is usually a good thing, as it means your cash isn't just sitting on a shelf collecting dust.
- Actionable Insight: To boost turnover, identify products that haven't sold in 90 days. Consider a small discount or bundle them with a popular item to get them moving.
- Perfect Order Rate: This is the ultimate report card for a supply chain. It measures the percentage of orders that show up at the right place, with the right stuff, at the right time, in perfect condition, and with all the correct paperwork.
- Actionable Insight: To improve this, start with one component: damage-free delivery. Ask your team to track every instance of damaged goods for a month. This focus will reveal if you have a packaging, handling, or carrier problem.

Navigating Common Supply Chain Challenges
Even the most meticulously planned supply chain is going to hit some turbulence. It’s just the reality of the modern world. Disruptions aren't a matter of if, but when. Truly understanding what is supply chain management is about preparing for these inevitable hiccups, whether it's a sudden global crisis or the slow, steady creep of rising costs.
These problems can send massive shockwaves through the entire system. Just look at the global microchip shortage that kicked off in 2020. A perfect storm of factory shutdowns and a huge spike in demand for electronics left the auto industry high and dry. Production lines ground to a halt, dealership lots were empty, and the price of used cars went through the roof. It was a masterclass in how a shortage of one tiny component can paralyze an entire industry.
You can dig into the specifics by reading the in-depth analysis of global supply chain risks. This forces a huge mental shift—it’s no longer just about being efficient, it’s about being resilient.
The Rising Tide of Volatility and Costs
Beyond those big, headline-grabbing shocks, supply chains are in a constant battle with volatility. Fuel prices can jump overnight and completely blow up your transportation budget. A sudden change in trade policy or a new tariff can make materials from a key country wildly expensive, throwing profit margins into chaos.
All this pressure means companies have to be incredibly nimble. You're constantly analyzing costs, hunting for ways to optimize without letting quality or speed suffer. This is where thinking ahead isn't just a good idea; it's a serious competitive advantage.
Building a Resilient Supply Chain Playbook
Anyone can point out a problem. It’s the companies that solve them that actually win. Building a truly resilient supply chain means having a proactive playbook—one that's focused on visibility, flexibility, and sustainability. It's about getting ready for the storm long before you see clouds on the horizon.
Here are three concrete strategies you can use to build that resilience:
- Diversify Your Supplier Base: Putting all your eggs in one basket by relying on a single supplier is a massive risk, especially if they're in one geographic region. A smarter move is to identify, vet, and build relationships with alternate suppliers in different locations.
- Practical Example: A bicycle manufacturer sources its frames from Vietnam but also has a qualified backup supplier in Mexico. When a shipping crisis slows down Pacific routes, they can quickly shift a portion of their orders to Mexico to keep production lines running.
- Embrace Track-and-Trace Technology: You can't manage what you can't see. Bringing in technologies like IoT sensors and blockchain gives you a real-time, bird's-eye view of your entire operation.
- Practical Example: A pharmaceutical company places IoT sensors on shipments of vaccines. These sensors monitor the temperature in real-time and send an alert if it goes outside the safe range, allowing them to intervene before the product is ruined.
- Adopt Sustainable and Circular Practices: Sustainability isn't just a buzzword anymore; it's a core business strategy. By adopting circular economy principles—like designing products that are easy to repair, refurbish, or recycle—you not only meet that demand but can also open up new revenue streams and slash waste.
- Practical Example: Patagonia's "Worn Wear" program encourages customers to trade in used gear for store credit. Patagonia then repairs, cleans, and resells the items, reducing waste and creating a new revenue stream from the same product.
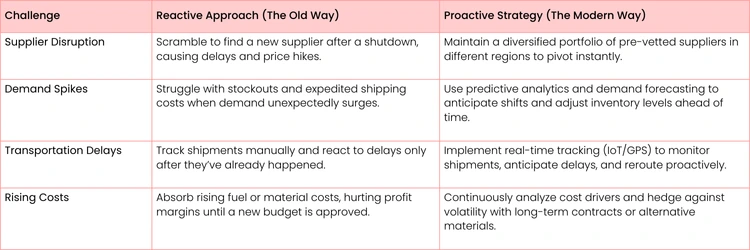
Comparing Proactive vs Reactive SCM Strategies
This table breaks down how traditional, reactive responses to common issues stack up against forward-thinking, proactive strategies.
As you can see, the modern approach is all about anticipation and preparation, turning potential disasters into manageable bumps in the road. Making these kinds of changes isn't always easy and often requires a big cultural shift inside a company. If you're running into roadblocks, this article on overcoming resistance to change has some practical advice for getting your team on board.
Real-World Examples of SCM Excellence
Theory is one thing, but seeing supply chain management in the wild is where the real lessons are. To truly grasp its power, let's look at the playbooks of two companies that have turned their supply chains into legendary competitive advantages.
They operate in completely different industries but share a common mastery of SCM principles. These examples show how a well-oiled supply chain isn't just a back-office function—it's the engine that drives an entire business.
Zara: The Masters of Speed and Agility
The fashion world moves at a blistering pace, and no one has weaponized speed quite like Zara. Their whole "fast fashion" model is built on an incredibly nimble supply chain that can take a design from a sketch to a store floor in as little as three weeks. For perspective, traditional retailers can take six months or more.
How on earth do they pull that off? It comes down to a few key decisions:
- Localized Manufacturing: Instead of sending all production to low-cost countries far away, Zara produces over 50% of its trendiest items in Spain, Portugal, and Morocco. This proximity gives them unbelievable control and slashes shipping times.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Every store manager has a tablet to send daily feedback on what’s selling and what’s collecting dust. That real-time data goes straight to Zara's design headquarters, letting them quickly make more of what customers actually want and avoid getting stuck with racks of unwanted clothes.
- Centralized Distribution: Almost every piece of clothing Zara makes passes through a massive, highly automated distribution center in Spain. From there, shipments go out to stores around the world twice a week, keeping a constant flow of fresh styles on the racks.
Actionable Insight from Zara: Use customer feedback as a direct input for your inventory. Even simple actions, like asking your front-line staff what questions customers are asking, can provide valuable clues about future demand.
Apple: The Architects of Scale and Precision
On the other end of the spectrum is Apple, a company that runs one of the most complex and powerful global supply chains ever built. While Zara is all about speed, Apple’s model is built on precision, scale, and iron-clad supplier relationships. They launch blockbuster products to millions of eager customers on the exact same day—a mind-boggling feat of coordination.
Apple's mastery comes from a few core strategies:
- Command of Supplier Relationships: Apple doesn't just buy parts; it deeply integrates with its suppliers. By placing enormous, long-term orders, it locks in amazing pricing and dedicated production capacity that its competitors can only dream of.
- Mastery of Logistics: To pull off flawless global product launches, Apple pre-positions inventory in key hubs around the world weeks ahead of time. It's famous for buying up huge chunks of available air freight capacity to make sure new iPhones and MacBooks hit shelves everywhere, all at once.
- Obsessive Secrecy and Control: Apple’s supply chain is famously secretive to prevent leaks before a big announcement. This tight control extends to every tiny component from hundreds of different suppliers, ensuring that their famously high quality standards are met without fail.
Actionable Insight from Apple: For your most important products or components, focus on building a deep, collaborative relationship with a key supplier. Regular communication and long-term planning can lead to better pricing, quality, and reliability than simply chasing the lowest bid.

Exploring Careers in Supply Chain Management
The world of supply chain management is a sprawling, fast-paced field that's absolutely vital to the global economy. It's a perfect fit for sharp, strategic thinkers who love solving complex puzzles. Because SCM covers everything from sourcing raw materials all the way to that final "knock on the door" delivery, there's a huge variety of roles for different skill sets—whether you're a data whiz who loves crunching numbers or a master negotiator who thrives on high-stakes deals.
These aren't just logistics jobs; they're about being a problem-solver on a global scale. Professionals in this space are constantly figuring out how to make massive, interconnected systems faster, stronger, and more cost-effective. It's no surprise that the demand for skilled talent is always high. Companies know a top-tier supply chain isn't just a department—it's a powerful competitive weapon.
Key Roles in the Supply Chain World
While you’ll find a ton of different job titles out there, most positions fall into a few core areas. Each one demands its own unique mix of technical know-how and people skills to really succeed.
Here are a few of the most common and impactful career paths you'll find:
- Logistics Manager: This is the person who orchestrates the physical movement of goods. They're in charge of transportation, warehousing, and inventory, making sure products get exactly where they need to be, right on time and without breaking the bank.
- Procurement Analyst: Focusing on the "source" part of the chain, these analysts are the experts in finding the best suppliers, hammering out contracts, and managing those crucial relationships. Their mission is to lock down high-quality materials at the best possible price.
- Supply Chain Consultant: Think of these pros as supply chain detectives. They parachute into different companies to diagnose weak spots in their operations. After a deep dive, they recommend smart strategies to boost efficiency, slash costs, and build a more resilient network.
A career in supply chain management puts you right at the heart of how a business actually works. Every single decision you make—from picking a supplier in another country to optimizing a local delivery route—directly impacts the company's bottom line and keeps customers happy.
How to Build Your SCM Career
Breaking into this field is all about blending foundational knowledge with real-world, practical skills. Your first step should be to get a solid grip on the core principles of SCM. A great way to prove your expertise and catch an employer's eye is by earning certifications from respected organizations like APICS (their Certified in Planning and Inventory Management, or CPIM, is a big one).
But formal credentials are just part of the picture. You absolutely have to sharpen specific abilities. Strong analytical skills are non-negotiable—you'll be swimming in data and need to spot trends and opportunities. Just as important is your ability to think on your feet and solve problems, because disruptions are a guaranteed part of the job. Getting some hands-on experience, even through an internship, gives you priceless context that you just can't learn from a textbook.
For anyone trying to map out a clear path forward, looking into professional career development resources can give you a structured roadmap to landing the role you want.
Frequently Asked Questions About SCM
Even with a solid grasp of the basics, a few questions always seem to come up. Let's tackle the most common ones to clear up any confusion and add some practical insights.
What Is the Difference Between Logistics and SCM?
This is probably the most common question we get, and it’s a great one. The simplest way to see it is that logistics is just one (very important) piece of the much bigger SCM puzzle.
Logistics is all about the hands-on movement and storage of goods. Think trucks, warehouses, and keeping track of inventory—it's the tactical side of getting things where they need to go. SCM, on the other hand, is the grand strategy. It covers a product's entire journey, from sourcing raw materials and manufacturing to managing relationships with every single partner along the way. Logistics fits right inside that framework.
In short: Logistics is about getting things from A to B efficiently, while SCM is about designing and managing the entire system that makes that journey possible in the first place.
How Can a Small Business Improve Its Supply Chain?
You don't need a massive budget to make a huge difference. For small businesses, focusing on a few high-impact areas can bring incredible improvements.
- Actionable Insight 1: Map your process. Use a whiteboard or a free online tool to draw a simple flowchart of your current process from order to delivery. This visual map will instantly reveal where bottlenecks and delays are hiding.
- Actionable Insight 2: Build supplier partnerships. Instead of always chasing the lowest price, have a conversation with your most reliable supplier. Ask if they offer discounts for early payment or larger orders. A strong relationship is more valuable than saving a few cents.
- Actionable Insight 3: Use simple tech. You don't need a full ERP. Start with cloud-based inventory software (many have free or low-cost plans). This is a game-changer for preventing stockouts and avoiding the cost of holding unsold products.
- Actionable Insight 4: Gather basic data. Track three things for a month: your on-time shipping rate, your order accuracy (did the customer get exactly what they ordered?), and your top reason for customer complaints. This simple data will tell you exactly where to focus your efforts.
Why Is the Reverse Supply Chain Important?
The reverse supply chain—often called reverse logistics—is everything that happens after a customer buys a product. This covers returns, repairs, recycling, and responsible disposal. It used to be an afterthought, but now it's absolutely critical for a couple of big reasons.
First up is customer loyalty. A clunky, difficult, or expensive returns process can turn a customer against your brand for good.
- Practical Example: Online shoe retailer Zappos built its brand on a famously easy, no-questions-asked 365-day return policy. This turned a potential point of friction into a key reason customers trusted them and kept coming back.
Second, it's about sustainability and recapturing value. An effective reverse supply chain lets you refurbish and resell returned items, which is a direct boost to your bottom line.
- Practical Example: When a customer returns a printer with a minor defect, the manufacturer can inspect it, replace the faulty part, and sell it as a certified refurbished product at a lower price, recouping most of the original cost and preventing it from ending up in a landfill.
Ready to build the skills for a successful career in this dynamic field? At Uplyrn, we provide expert-led courses and practical resources designed to help you master the complexities of supply chain management. Start your learning journey and transform your professional future today.


Leave your thoughts here...
All Comments
Reply