How to Write a Business Plan That Actually Works

Before we dive into the nitty-gritty of each section, let's get one thing straight: a business plan isn't some dusty, formal document you write once and forget. Think of it as your strategic compass. It's the living, breathing roadmap that guides every single decision you make, from product development all the way to chasing down funding.
Jump To Section

Earn As You Learn
Earn 25% commission when your network purchase Uplyrn courses or subscribe to our annual membership. It’s the best thing ever. Next to learning,
of course.
Your Business Plan is Your Strategic Compass
Too many entrepreneurs fall into the trap of thinking a business plan is only for getting a loan. While it’s definitely critical for that, its real power is in building a solid foundation for growth. A great plan forces you to get brutally honest with yourself and ask the tough questions before you sink a ton of time and money into a venture.
It’s the tool that transforms a brilliant idea into a viable business.
- Practical Example: Let’s say you have an amazing concept for a new online course teaching digital marketing. That's a great starting point. The business plan pushes you to dig in—to analyze that your target audience is freelance creatives, not corporate teams, to size up your competitors, and to realistically project that it will cost you $5,000 in video equipment and editing software to create the course. This process turns a hopeful daydream into a calculated business move.
From Idea to Action
Taking a concept from a spark of an idea to a thriving business is a journey, and a business plan ensures you're making deliberate choices, not just reacting to whatever comes your way. We've seen it time and time again. The process generally breaks down into a few key stages.
- Decide: This is the genesis. You’re defining your core mission and, most importantly, the specific problem you're solving for your customers.
- Actionable Insight: Don't just state your mission. Write a one-sentence "problem statement" from your customer's perspective. For example: "Freelance designers struggle to find affordable, project-based marketing training that fits their schedule."
- Align: Next, you start connecting the dots. This is where you align your operations, your marketing plan, and your financial model with that core mission.
- Grow: With a solid plan in place, you can finally think about scaling strategically and capturing new market opportunities with confidence.
These phases aren't just a checklist; they build on each other in a continuous cycle of strategic development.
This process shows that a business plan is a dynamic framework, not a one-and-done task. It’s your compass, and it needs to be tailored to your specific venture. This kind of foundational planning is central to what we call the startup blueprint for long-term success, because it’s what helps you sidestep those costly mistakes down the line.

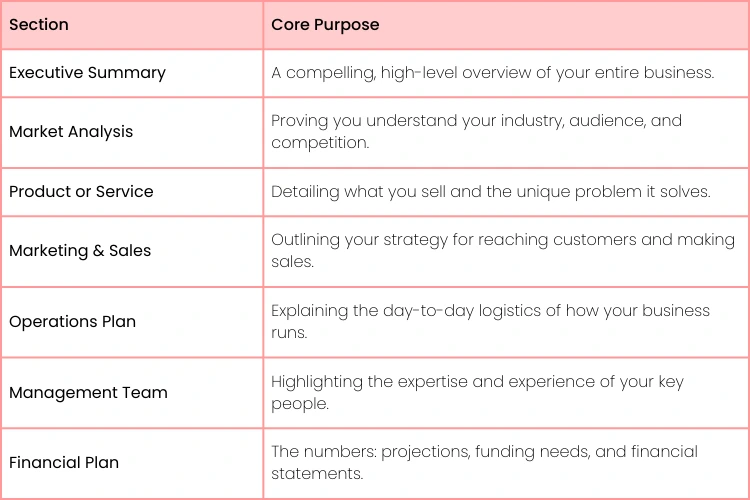
The 7 Core Components of a Winning Business Plan
Now, let's look at the essential pieces that make up a powerful business plan. While the specifics will vary, every truly effective plan is built on the same core components.
Think of these 7 sections as the chapters of your business' story. In the rest of this guide, we're going to break down exactly how to write each one, step-by-step.
Crafting an Executive Summary That Gets Read
Think of your executive summary as the movie trailer for your business plan. It's the very first thing an investor or lender sees, and if it doesn’t immediately hook them, they probably won't stick around for the main feature. This isn't just an intro; it's your one shot to make a powerful first impression.
The goal is to distill your entire vision into a tight, compelling narrative. You need to answer the big questions right out of the gate: What problem are you solving? What's your solution? Who are your customers? And, most importantly, why will this business make money?
- Actionable Insight: Write this section last. It's so much easier to summarize everything once you’ve already wrestled with the details of your market analysis, financials, and operations. Trying to write it first is like trying to write the blurb for a book that doesn't exist yet. Keep it to one page, maximum.
From Bland to Compelling
Let's make this real. Imagine a fictional startup called "ConnectSphere" which has built a new project management tool.
Here's a typical first draft—bland and instantly forgettable:
ConnectSphere is a new software company that has created a project management platform. Our product has many features to help teams collaborate. We are seeking funding to grow our user base."
This tells the reader nothing of substance. It’s generic, lacks punch, and won't get you a second look.
Now, let's inject some life and data into it:
"For remote teams struggling with project delays caused by inefficient communication—a problem costing businesses an estimated $37 billion annually—ConnectSphere offers a streamlined collaboration hub. Unlike clunky, oversized platforms, our tool integrates task management, communication, and file sharing into one intuitive interface, boosting team productivity by an average of 25%. We are targeting small to medium-sized tech companies and are projecting $1.2M in annual recurring revenue by year three. We are seeking $500,000 to scale our marketing efforts and expand our development team."
See the difference? This version grabs you by starting with a massive, relatable problem backed by a hard-hitting statistic. It clearly defines the solution, names the target market, and presents a confident financial forecast. This is the kind of summary that makes an investor lean in and want to know more.
To nail this, you have to be crystal clear on your core value. Understanding how to craft your core message is key to making sure every single word in your summary works for you.

Conducting Market Analysis That Reveals Opportunity
A great idea is just that—an idea. To turn it into a business, you have to prove there’s a real market waiting for it. This section of your business plan is where you stop assuming and start proving. It’s your chance to show investors you’ve stumbled upon a genuine opportunity, not just a personal passion project.
Think of yourself as a detective. Your mission is to validate your entire venture with cold, hard facts. It’s not enough to say your industry is huge. You need to tell a compelling story about where your specific business fits into that bigger picture. That means digging into industry trends, getting crystal clear on who your ideal customer is, and taking an honest look at your competition.
Sizing Up Your Market
First things first, let's talk numbers. You need to define your market from three different altitudes:
- Total Addressable Market (TAM): This is the big picture—the entire global revenue opportunity for your product or service.
- Serviceable Available Market (SAM): Now, zoom in a bit. This is the segment of the TAM you can realistically serve with your business model.
- Serviceable Obtainable Market (SOM): This is the ground-level view. It’s the portion of your SAM you can realistically capture in the first few years.
Practical Example: Imagine you're launching an e-commerce store specializing in sustainable home goods in the United States.
Your market breakdown might look something like this:
- TAM: The entire global market for home goods, valued at over $700 billion.
- SAM: The U.S. online market for home goods for consumers who prioritize eco-friendly products, estimated at $25 billion.
- SOM: The portion of that U.S. sustainable market you can realistically capture in your first three years, say $5 million, based on your marketing budget and initial brand reach.
Laying it out this way proves you've thought critically about scale and growth. This isn't just an academic exercise; strong market analysis is a massive factor in getting funded. Startups with well-researched plans secure funding 2.5 times more often. And in hot sectors, it's even more critical.
Profiling Your Ideal Customer and Competition
Okay, so you know the size of the pond. Now, who are the fish? This is where you create detailed customer personas.
Don't just list demographics like age and location. Go deeper into their psychographics.
- Actionable Insight: Create a persona profile that includes their goals, frustrations, and watering holes (where they hang out online). For our sustainable goods store, a persona isn't just "a woman, 30-40". It’s "Eco-Conscious Erin, a 34-year-old graphic designer who follows sustainability bloggers on Instagram, is frustrated by greenwashing, and is willing to pay a premium for ethically sourced products."
A deep understanding of your customer's motivations is your greatest competitive advantage. If you know why they buy, you can build a brand they'll love.
Next, it’s time to size up the competition. You need to identify both your direct competitors (other stores focusing solely on sustainable goods) and your indirect ones (think big retailers like Target or Amazon that have their own eco-friendly lines).
- Actionable Insight: Create a competitor matrix. List your top 3-5 competitors in a table. Create columns for key features like "Price Point", "Product Range", "Brand Voice" and "Marketing Channels". Rate each competitor and yourself. This visual tool instantly reveals gaps in the market where you can win. This is an area where a lot of businesses stumble; you can find out if your business might be doing competition analysis wrong. A thorough analysis will reveal the gaps in the market—and that’s exactly where your business can thrive.
Laying the Groundwork: Operations and Your Go-To-Market Plan
Alright, you’ve figured out who you’re selling to and what the market looks like. Now it’s time to get into the nitty-gritty: the "how". This is where your big idea starts to feel like a real, functioning business.
This section is all about connecting your day-to-day operations—how you’ll actually run the company—with your marketing and sales strategy—how you’ll get people to buy from you. Think of them as two sides of the same coin; one can't succeed without the other. They need to work together seamlessly to create a growth engine.
- Practical Example: Let’s say you’re opening a local coffee shop. The operations plan covers everything behind the counter: sourcing fair-trade beans from a specific supplier in Colombia, managing inventory of oat milk and pastries using Square for Retail, and creating a detailed training checklist for new baristas. It's the backstage work ensuring a perfect latte, every time. Your marketing plan is what gets people to walk through the door, like offering a "first coffee free" promotion via a targeted Facebook ad to people within a 2-mile radius.
Defining Your Daily Operations
Your operations section needs to map out your daily workflow from start to finish. Think about the entire process, from creating your product to getting it into your customer's hands. What are the non-negotiable activities that have to happen every day?
- Supply Chain: Where do your materials come from? Who are your go-to suppliers, and what are your backup plans? For our coffee shop, this means naming "Roast Masters Inc." as the primary bean roaster and "Artisan Beans Co." as the backup.
- Technology Stack: What software makes your business run? This could be your website platform (Shopify), payment processors like Stripe, or a simple CRM like HubSpot to track customer interactions.
- Team and Responsibilities: Who is doing what? Clearly outline the key roles, even if you’re wearing all the hats at the beginning.
- Actionable Insight: Create a simple organizational chart, even for a solo venture, listing key functions (e.g., CEO, Marketing, Operations) and who is responsible. It shows you understand what it takes to get the job done.
Nailing this down proves you’ve moved beyond the idea stage and are thinking about the practical, real-world execution of your business. A well-oiled operational machine is what allows you to deliver on the promises you make in your marketing. This guide on how to win with your business model digs deeper into building these essential frameworks.
Crafting Your Marketing and Sales Strategy
Now, let's talk about getting customers. Your go-to-market plan should be a direct, actionable playbook for reaching your target audience and convincing them to buy. Everything you do here should tie back to those customer personas you worked so hard on.
Don't just list a bunch of marketing tactics. Explain which channels you'll use and why they make sense for your specific audience.
- Practical Example: For the coffee shop targeting local professionals, the strategy would be a hyper-local SEO focus ("best coffee near me"), running targeted Instagram ads showcasing latte art to people who work downtown, and creating a "buy 10, get one free" loyalty program managed through your POS system.
Your marketing and sales strategy isn't just about making noise; it’s about creating a predictable system for generating revenue. It connects your product to the people who need it most.
When choosing your marketing channels, show that you're aware of what's happening in your industry right now. Sprinkling in statistics shows investors you've done your homework.
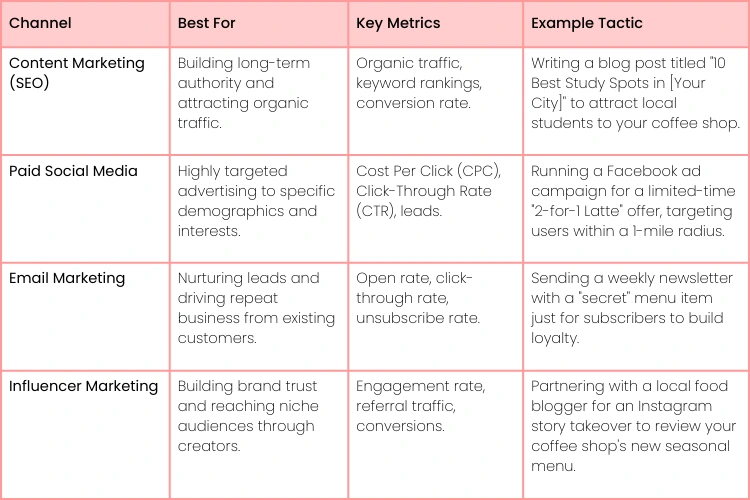
Choosing Your Digital Marketing Channels
Picking the right marketing mix is crucial, especially when you're working with a tight budget. You want to put your time and money where they'll have the biggest impact. The table below breaks down some popular digital channels to help you make an informed decision.
Ultimately, your go-to-market strategy should feel like a natural extension of your brand and a direct line to the customers you want to serve. Choose channels that align with where your audience spends their time and what they value.
Developing Financial Projections That Inspire Confidence
Numbers tell a story, and in your business plan, the financial section is the grand finale. This is where you connect all the dots—your vision, market analysis, and operational strategy—and translate them into cold, hard figures.
For any potential investor, this section isn't just about crunching numbers. It's about seeing if you have a firm grip on the financial reality of your business and whether it has a viable future.
Your main goal here is to build a realistic forecast for your first three to five years. Don't just pull numbers out of thin air. Every single projection you make needs to be supported by a clear, logical assumption you've already documented elsewhere in the plan.
- Actionable Insight: Create an "Assumptions" page or section right before your financial statements. Here, you explicitly state things like, "We project a 2% conversion rate on website traffic, based on industry averages for e-commerce" or "We assume a 5% monthly customer churn, which is standard for SaaS startups in their first year."
The Three Core Financial Statements
Think of your financial projections as being built on three core documents. Together, they paint a complete picture of your company's financial health.
- Income Statement (P&L): This is your profitability report card. It shows revenues, costs, and profits over a set period—usually monthly for the first year, then quarterly or annually. It answers the most basic question: "Are we making any money?"
- Cash Flow Statement: For a new business, this is arguably the most critical document of the three. It tracks the actual cash coming in and going out of your company. It’s what helps you see cash shortages before they happen and manage your day-to-day funds.
- Balance Sheet: This is a snapshot of your business's financial health at a specific moment. It lays out what you own (assets) versus what you owe (liabilities), giving a clear view of your company's net worth.
These statements aren't just for show. To truly master your financials, you need to use them as internal management tools to track how you're performing against your own goals.
A Practical Example: A SaaS Startup
Let's put this into practice. Imagine you're launching a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) business. Your financial world will revolve around metrics like monthly recurring revenue (MRR), customer acquisition cost (CAC), and lifetime value (LTV).
In your projections, you'd break it down like this:
- CAC Calculation: You plan to spend $5,000 on marketing in one month and acquire 50 new customers through Google Ads and LinkedIn outreach. That makes your CAC $100 per customer.
- LTV Calculation: Your subscription is $30/month, and your data (or industry comparable data) suggests an average customer sticks around for 24 months. That puts your LTV at $720.
When you present this LTV to CAC ratio (7.2 to 1), it immediately tells an investor that for every dollar you spend acquiring a customer, you expect to get more than seven dollars back. That’s the kind of data-driven storytelling that gets people excited.
The real strength of your financial projections isn’t in the final numbers, but in the logic of your assumptions. Clearly explain why you think your conversion rate will be 2% or your customer churn will be 5%. This transparency is what turns a wild guess into a credible forecast.
Structuring Your Funding Request
If the whole point of this business plan is to get funding, this is where you make the ask. Be direct, be specific, and be confident.
A vague request like, "We need $200,000 for growth" is an instant red flag for investors. It shows you haven't thought it through. Instead, break down exactly where every dollar is going:
- $75,000 for product development (hiring one senior engineer for 12 months at a $75k salary).
- $100,000 for marketing (to acquire 1,000 new customers over 12 months, based on our projected $100 CAC).
- $25,000 for operational overhead (software subscriptions, legal fees, and a 3-month cash runway).
Solid projections matter. Studies show that startups with a formal business plan raise 30% more capital on average. Investors are scrutinizing financials more than ever. They want to see that you've factored in key market drivers. This level of detail proves you've done your homework.

Spotting (and Fixing) Common Business Plan Mistakes
You’ve put in the hours and crafted a business plan. Awesome. But even the most buttoned-up plans can stumble over a few common, easily avoided tripwires.
Learning to spot these weaknesses before an investor does is a game-changer. Let's walk through some of the classic blunders so you can polish your plan and present it with confidence.
The "Too Good to be True" Financials
This is probably the number one mistake: financial projections that are wildly optimistic. It's so easy to get swept up in the excitement of your idea, but numbers that look like they belong in a fantasy novel will get your plan tossed aside immediately.
Investors have seen thousands of "hockey-stick" growth charts. They can sniff out unrealistic forecasts from a mile away.
- Practical Example: A plan for a subscription box startup projecting $5 million in revenue in its first year. How? By assuming a 10% website conversion rate from day one, when the industry average for new e-commerce sites is closer to 1-2%. That number completely ignores the brutal reality of customer acquisition costs and high churn rates.
- Actionable Insight: Create three financial scenarios: a conservative case (worst-case), a realistic case (most likely), and an optimistic case (best-case). This demonstrates that you've considered potential risks and aren't just betting on a perfect outcome. Base your realistic projections on solid market research, data from comparable businesses, and assumptions you can actually defend.
The "We Have No Competition" Myth
Another classic error is a shallow or, even worse, dismissive competitor analysis. If you write "we have no competition" or claim your idea is so revolutionary that it's untouchable, you've just raised a massive red flag.
Every single business has competitors, whether they're direct or indirect. Ignoring them doesn't make you look unique; it makes you look naive about the market you're trying to enter.
A weak analysis just lists who's out there. A strong one digs deep into their strengths, weaknesses, and market position to show exactly where your opportunity lies.
- Weak: "Our competitors are Company A and Company B. We're better because our product has more features."
- Strong: "Company A dominates with 70% market share but is notorious for poor customer support, with an average response time of 48 hours. We will offer 24/7 live chat support and will specifically target their dissatisfied customer base in our launch campaign by running ads against keywords like '[Company A] alternative'."
It’s not about just naming your rivals. It’s about proving you understand the competitive battlefield well enough to win your corner of it.
The Unfocused "Everything to Everyone" Plan
Finally, a lot of business plans fail because they're just all over the place. A plan that lacks a clear focus—on its target audience, its core value proposition, or its revenue model—comes across as scattered and amateurish.
You can't effectively target "everyone between the ages of 18 and 65". It's impossible.
- Actionable Insight: Start with a very specific niche, your "beachhead market". A business plan for a vegan bakery shouldn't just vaguely mention "offering baked goods". It should get specific: a focus on gluten-free, organic birthday cakes for health-conscious parents of young children in a specific city. You can always expand later, but proving you can win one small, focused market first gives your entire plan more credibility and power.
Got Questions About Your Business Plan?
Even with a solid outline, it’s natural to have a few lingering questions. It’s one thing to know the sections you need to write, but it's another thing entirely to feel confident about the nitty-gritty details.
Let's clear up some of the most common sticking points entrepreneurs run into.
How Long Should a Business Plan Be?
Honestly, focus on impact, not page count. There's no magic number.
While a traditional plan aimed at investors or a bank loan officer often settles in the 20-30 page range, a simple internal plan meant to keep your team aligned could be a lean, one-page document. The goal is to be thorough but direct. Give them everything they need to know without burying them in fluff.
- Actionable Insight: If you need a quick version for networking, create a one-page "Business Model Canvas". It visually lays out your key components—from customer segments to revenue streams—on a single sheet, forcing you to be concise.
Should I Use a Business Plan Template or Software?
They can be a huge help, especially if you're starting from scratch. Templates and specialized software give you a reliable structure, making sure you don’t forget any of the crucial pieces of the puzzle.
But here's the thing: never let a tool do your thinking for you. Use it as a guide, a framework, but make sure the final document is dripping with your specific vision, your research, and your voice. The real value comes from the quality of your strategic thinking, not from filling in the blanks.
- Practical Example: A template might have a section for "Marketing Strategy". Don't just write "Use social media". Specify: "We will use Instagram Reels to showcase our product in action, targeting followers of [Competitor X] and [Influencer Y], with a starting budget of $500/month."
How Often Should I Update My Business Plan?
Your business plan should be a living, breathing document—not a "write it and forget it" project that gathers dust on a shelf.
- Actionable Insight: Schedule a quarterly review of your business plan with your team (or by yourself). Put it on the calendar like any other important meeting. Compare your financial projections against your actual results and update your market analysis with any new competitor moves or industry trends.
Key moments that demand an immediate update include:
- Landing a new round of funding
- Launching a major new product or service
- A new competitor shaking up the market
- Pivoting your core business model
Keeping your plan current ensures it stays a relevant, valuable tool that actually guides your decisions. Otherwise, it just becomes an old souvenir from your startup's early days.
Ready to turn that business idea into a rock-solid plan? At Uplyrn, we've got the expert-led courses and resources to help you build a strong foundation for success. Whether you're trying to nail your financial projections or craft a marketing strategy that gets results, we're here to help you learn the skills that matter. Explore our business courses and start building your future today.


Leave your thoughts here...
All Comments
Reply